Users
How to Identify and Manage Users
Logging-in users
Overview
A logged-in user is someone who can contact your support team only after providing appropriate credentials. If you have logged-in users, we highly recommend passing the user's identifiers (user ID and/or email) using the Login API so that your Agents can provide a personalized support experience to your users, no matter which device your end user is using. Using the Login API also ensures that a user's conversations are available only to them when they log in.
What to provide as identifiers
You can provide either userID and/or userEmail to identify your users. We highly recommend using a user ID to identify your users. However, if you use emails to identify your users, then you should pass them in the userEmail field.
The following logic applies when you use both userID as well as userEmail:
- When looking up users, the priority of `userId` is higher than that of `userEmail`
- When the user ID matches an exisiting user, that user's email will be updated (if the email is provided)
- When the email matches an existing user, the following logic applies:
- If the user ID does not exist for a user matched by email, then the user ID will be added for that user (if a user ID is provided)
- If the user ID already exists on the user matched by email, then a new user will be created (if a different user ID is provided)
How to use
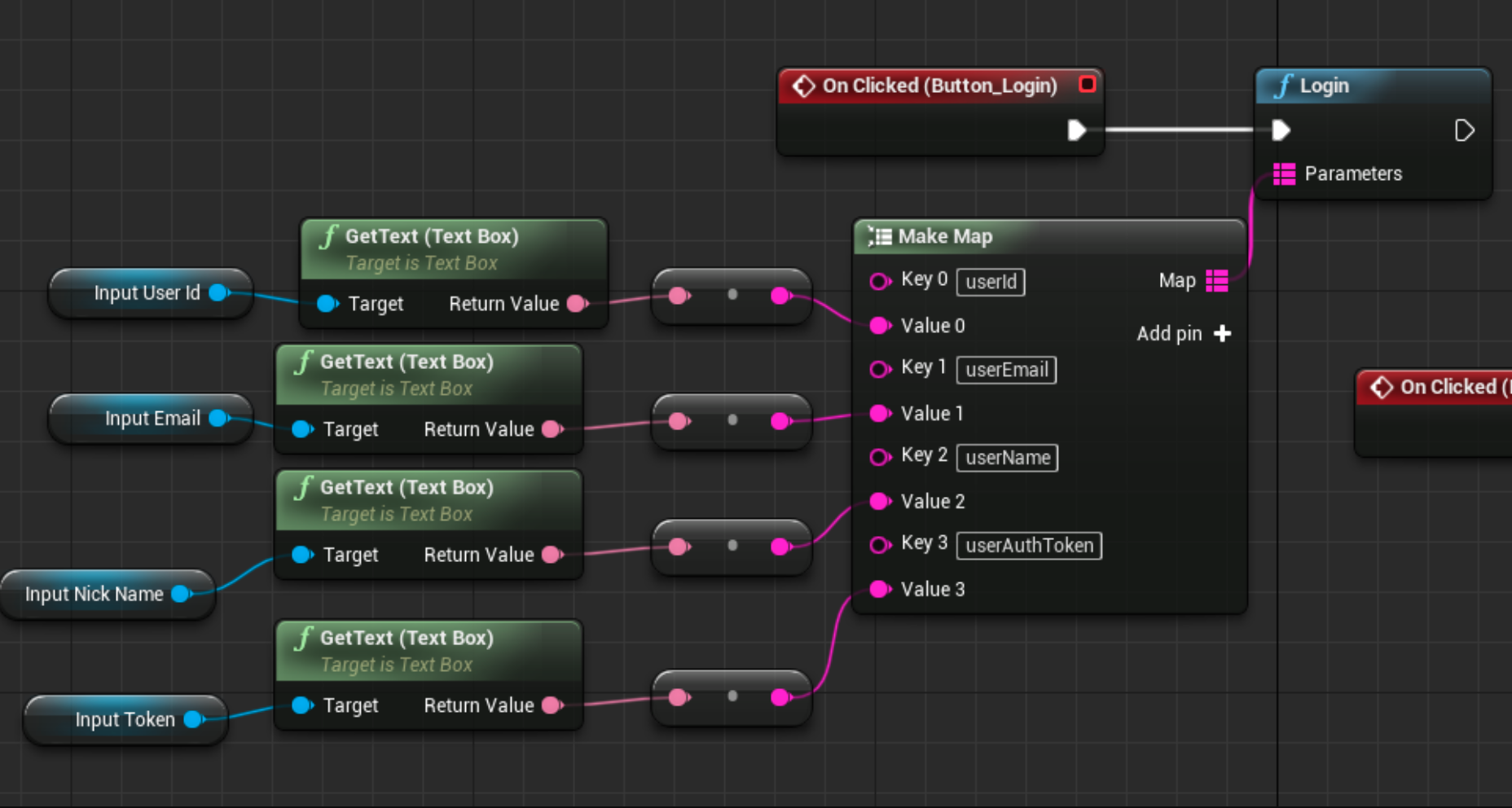
You should call Helpshift SDK's Login API whenever the user successfully logs into your app. The Login API takes the following parameters:
| Parameter | Require/Optional | SDK Description | Inportant Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| userName | Optional | Provide the name you'd like your Agents to use when interacting with end users. If you don't know the user's name, you can leave it blank, and the Identity Bot (when enabled) will ask that user for their name. If you provide a value, the Identity Bot will not ask the user for their name again. | Max length: 255 characters. Values larger than this will be truncated. |
| userId | Required as an identifier if email is not provided | A user's unique identifier. User IDs must be unique. You should not use the same user ID for different users. |
|
| userEmail | Required as an identifier if the user ID is not provided | A user's email address. If you don't know the user's email, you can leave it blank and the Identity Bot (when enabled) will ask the user for their email. If you provide a value, then the Identity Bot will not ask the user for their email again. |
|
| userAuthToken | Optional | A user authentication token generated via Hash-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) using SHA256. You should provide an HMAC Digest if you want to ensure that 3rd parties cannot file issues on behalf of your users or update their properties. Details here. |
|
In order to create a logged-in user in Helpshift, the use of either userId or userEmail is required.
Logging out users
Overview
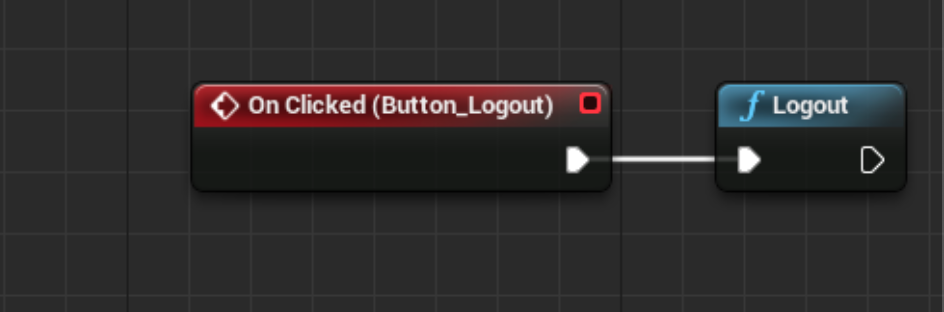
Once a user logs out from your app, you should call the Helpshift SDK's Logout API to ensure no one else can view this user's conversations.
The Logout API is expected to be used in conjunction with the Login API.
How to use
Anonymous users
- ClearAnonymousUserOnLogin() API is deprecated from v10.2.0. We have introduced a new API ClearAnonymousUserOnLogin(bool clearAnonuser) to clear anonymous users.
Overview
An anonymous user is someone who can access the app without a userId or userEmail. If a user identifier (user ID and/or email) is not passed via the Login API, then Helpshift assumes that the user is an anonymous user and is not currently logged in.
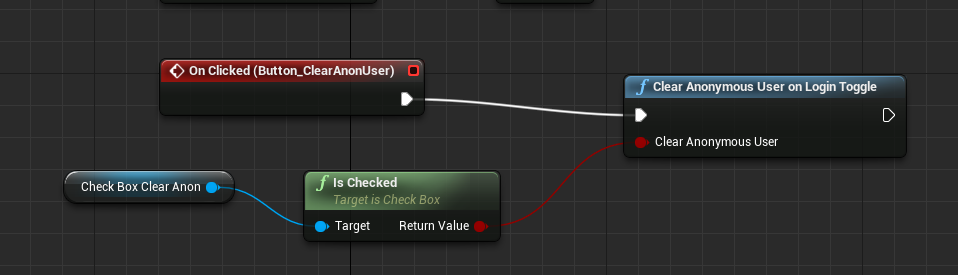
If your use case involves multiple logged-in/anonymous users using the same device and discussing info during support conversations (which you ideally wouldn't want to be shared across logins), you should use the HelpshiftLibrary::ClearAnonymousUserOnLoginToggle(boolean clearAnonymousUser) API.
If clearAnonymousUser is true – anonymous users are cleared whenever any user logs in. Once cleared, such users (and their conversations) cannot be fetched again.
If clearAnonymousUser is false – anonymous user data will be saved and if a logged-in user is logged out, you will see anonymous user’s conversation history.
- The ClearAnonymousUserOnLogin API does not impact the logged-in user's experience at all
- The ClearAnonymousUserOnLogin API will only work if called from logged-in mode.
Verifying the identity of users
Configuring identity verification in your app
Overview
User Identity Verification is a security measure that verifies that all requests made from your app to Helpshift are coming from authentic end users. This prevents 3rd parties or hackers from impersonating your users. You can learn more about User Identity Verification and the steps to configure it here.
In order to ensure your users are verified, you should provide a 'user authentication token' with the Login API at the time of initialization. You can find the steps to generate a 'user authentication token' here. The 'user authentication token' is an HMAC Digest, which is generated via HMAC using SHA256.
Sending the HMAC Digest to verify users' identity
You can send the 'user authentication token' with the Login API call. If Identity Verification is enabled on the Helpshift Dashboard (documentation here), Helpshift recalculates the unique 'user authentication token' using the shared secret key, and compares the 'user authentication token' sent by you to the recalculated value. If they're equal, then the user's identity is verified, and they are able to file Issues.
You can use the userAuthToken key to pass into the Login() API map.

If the secret key is regenerated for an app on the Dashboard, you should ensure you update your endpoint code as well, in order to generate a valid 'user authentication token'. Following this, your Admins should delete the old secret key from the Dashboard in order to ensure requests using a 'user authentication token' generated using the old secret key become invalid.
If EnableFullPrivacy is 'On', then the 'user authentication token' should be generated only on the user ID.
Identity verificaiton failure
Overview
When Identity Verification is turned 'On' and a login request is made with no 'user authentication token' or with an invalid 'user authentication token', identity verification will fail. If identity verification fails, the following will hold true:
- Anonymous users (users for whom the developer is not providing any identifiers) are always able to file Issues.
- Logged-in users (users for whom the developer is providing an identifier such as user ID or email) will not be able to file Issues or see conversations if they are unverified. Unverified logged-in users will see an error on the conversation UI.
If the logged-in users are verified (i.e. a valid 'user authentication token' is provided), they are able to see the previous issue or create a new issue. The UI for verified, logged-in users looks & works exactly the same as it would if 'Identity verification' were turned off. Only unverified users get impacted as listed above.
How to use the failure delegates
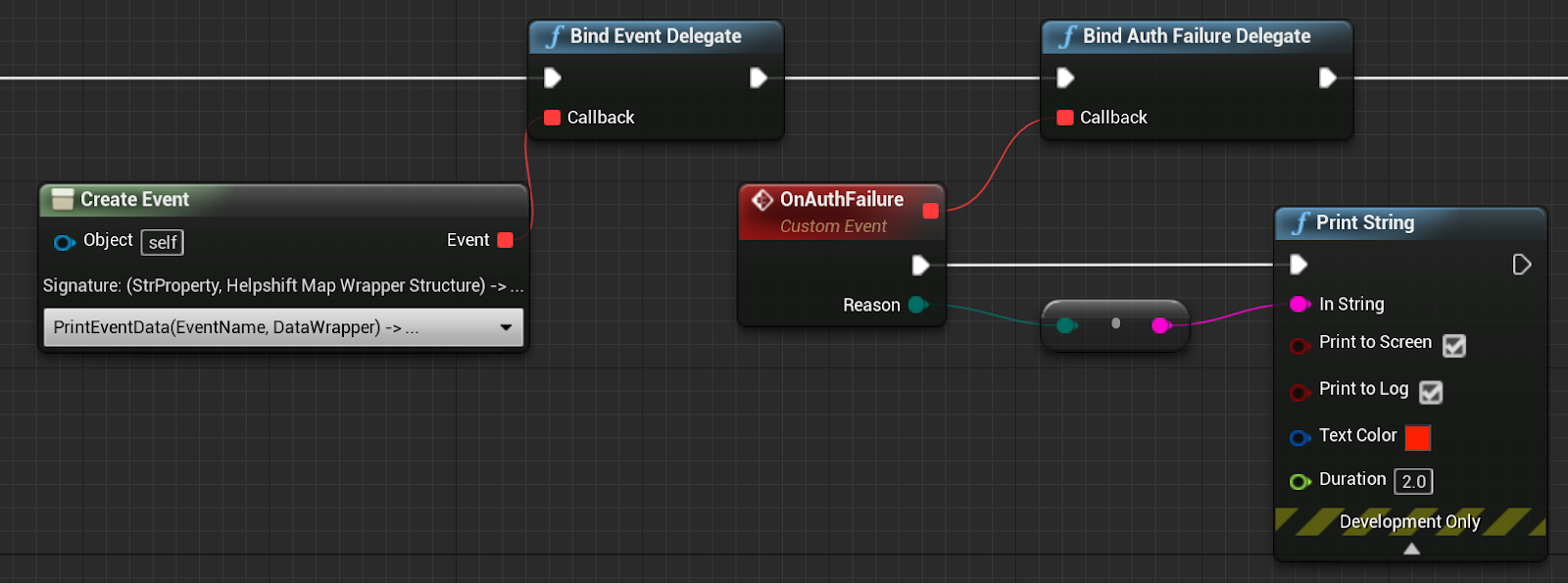
If identity verification fails, the SDK will invoke the AuthenticationFailedForUser(...) delegate to notify the application of the failure:
You can find these values in the HelpshiftLibrary.h file.
| Authentication failure reason | When is it called | When to use |
|---|---|---|
| EHelpshiftAuthenticationFailureReason .REASON_AUTH_TOKEN_NOT_PROVIDED | When no 'user authentication token' is provided | If you do not plan on sending a 'user authentication token', but plan on implementing it in the future, you can use this failure delegate to show your own alerts to the user, such as a prompt to update the app. You may want to use this if you are using the login API without the 'user authentication token', since these users will be considered unverified once 'Identity Verification' is enabled on the Dashboard. Using this delegate is completely optional - Helpshift will prevent unverified users from being able to file Issues, as mentioned previously. |
| EHelpshiftAuthenticationFailureReason .REASON_INVALID_AUTH_TOKEN | When the 'user authentication token' is invalid | If the HMAC Digest being provided via login API is invalid, then Helpshift will prevent the users from filing Issues. The 'user authentication token' can be invalid if:
|
| EHelpshiftAuthenticationFailureReason.UNKNOWN | When the reason for the authentication failure is unknown |
The authentication failure reason is wrapped in an enum EHelpshiftAuthenticationFailureReason Example:
Use BindAuthFailureDelegate(const FHelpshiftAuthFailureDelegate& Callback);